You may see the message Code: 9999, Error: Execution error in the pm_error.log file during an SSH key rotation or change, with no obvious hints as to the cause. One possible reason for this issue is related to the SSH key format. Starting from OpenSSH 7.8, the private key is not output in OpenSSL’s PEM format by default, which is one the format accepted by CyberArk as an SSH key.
Continue reading “CyberArk Account Password Change Failed with Code: 9999, Error: Execution error”Category: Troubleshooting
Workaround to connect the server with RDP Licenses not available Error
You might sometimes see the error like this when trying to connect to Remote Desktop Session Host server
The remote session was disconnected because there are no Remote Desktop License Servers available to provide a license.
Continue reading “Workaround to connect the server with RDP Licenses not available Error”Resolving winget not recognized error when running with the System Account
Although winget exists on your system, but when you try to run the winget with system account (or using the scheduled task with the system account) and you see this error.
winget : The term ‘winget’ is not recognized as the name of a cmdlet, function, script file, or operable program. Check the spelling of the name, or if a path was included, verify that the path is correct and try again.
Continue reading “Resolving winget not recognized error when running with the System Account”Esxi Kickstart file in the network location problem during Scripted installation with CDROM
If the ks.cfg file is skipped although it’s placed in a correct network location for the semi-automated installation (booted from CDROM), you may need to check these steps in case you missed them.
Continue reading “Esxi Kickstart file in the network location problem during Scripted installation with CDROM”The WS-Management service cannot process the request. Cannot find the Microsoft.PowerShell session configuration in the WSMan: drive on the…
After updating to Ps 4.0, I found some windows hosts are encountering the following errors when I run Invoke-Command to check the powershell version. See Fig-1.
Connecting to remote server X.X.X.X failed with the following error message : The WS-Management service cannot process the request. Cannot find the Microsoft.PowerShell session configuration in the WSMan: drive on the X.X.X.X computer.
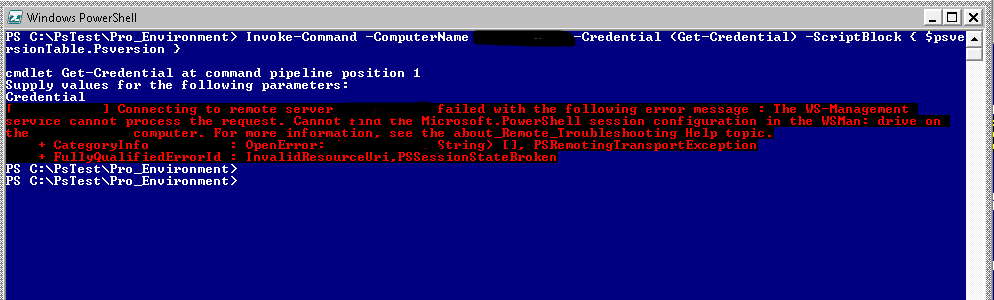
Continue reading “The WS-Management service cannot process the request. Cannot find the Microsoft.PowerShell session configuration in the WSMan: drive on the…”
High Memory Usage with w3wp.exe in Exchange Server
w3wp.exe process is an IIS web application process to handle the client request for the application pool. Exchange server services heavily utilized w3wp process not only to handle users request from external but themselves make web service requests among Exchange server members using virtual directories (Owa, OAB & Powershell etc) and respective App pools. Unless you have not configured periodic recycling for Application Pool, you may need to do manual recycle to avoid memory leaks. Microsoft Technet states that: Continue reading “High Memory Usage with w3wp.exe in Exchange Server”
Recover Crashed Exchange 2013 Mailbox Server in DAG
Recovering a crashed mailbox server in a Database Availability Group (DAG) is a straightforward process using the setup.exe /m:RecoverServer command. However, to ensure a smooth recovery, you need to follow certain steps. Here’s an overview of the recovery process, which I will explain in detail later:
Change grayed out Windows Service Startup Option
You might sometimes encounter grayed-out services, particularly in scenarios like antivirus programs where certain services are intentionally safeguarded against tampering for security purposes, can pose challenges in managing your system effectively. However, there are strategies you can employ to navigate this hurdle and regain control over these services.
Continue reading “Change grayed out Windows Service Startup Option”