It is the updated version [v2.1] of the script that will create users in nested OU. If you do not know how to use this script, you can see here.
I made some update changes so users ‘Names’ do not need to be unique in domain level but only in each OU. Continue reading “Updated v2.1: Create Users in New AD Domain with Old Users’ Domain Info”
Category: Powershell
Create Users in New AD Domain with Old Users’ Domain Info
It has been nearly 2 years that I wrote the script to create new AD users with the automatic nested OU creation. The original idea is to create the users from the csv file in which AD users properties are defined. The script now supports extracting the current users and OU information from old domain and use in the new domain. The script will prompt for the new domain name & passwords (optional) to put in the csv file. Continue reading “Create Users in New AD Domain with Old Users’ Domain Info”
Find who reset my password: The Powershell Script to Audit User Accounts Changes
Getting the account management activity is an essential process for auditing purpose. We can check it at the windows event log if the auditing for account management is enabled. To automate this tiresome job, I wrote this powershell script to make life easier.
This script will show you all the changes that admin made to the user/system account, such as the time when the password was reset and who reset the password; who added user to specified group; which attributes of user account was changed. Before running this script, you’ll have to enable auditing of account management to ‘Success’ in local security policy, for the enough of the time so that required events are collected. Don’t worry I have included the user’s option to enable from within this script. Continue reading “Find who reset my password: The Powershell Script to Audit User Accounts Changes”
Script to Log TCP Connections by Powershell
Logging TCP connection is useful for troubleshooting or for auditing purpose. You can use TCPView to view the real-time the incoming and outgoing TCP connections between servers and clients. To save the log into file, you need to use TCPLogView. But, the limitation is the duration of TCP capture, or based on log file size without actually doing the custom scripting. Windows has a built-in netstat command which can capture the TCP/UDP connection. So, with the help of powershell, I loop the execution of netstat command & capture the new TCP connection based on previous connections. With this script, you can capture new TCP connections to a specific time or until the log file size is reached to avoid the disk space consumption. Continue reading “Script to Log TCP Connections by Powershell”
A Quick Start Guide: How to Manage Veeam Backup & Replication 9 with Powershell
Most enterprise backup software has come with powershell support to make backup administrators life easier. In this post, we will play some veeam powershell
commands to backup/restore VMs or for listing current backup jobs. The veeam powershell has more cmdlets for advanced Vss aware backup (such as SQL, Exchange) which I do not cover here. Here, I will show only VM level backup/restore with powershell. Continue reading “A Quick Start Guide: How to Manage Veeam Backup & Replication 9 with Powershell”
Batch/Powershell: How to check Pending Computer Restart after Installing Windows Update
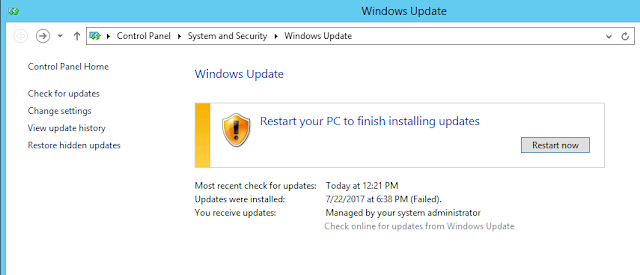
Some windows updates require a system restart after installation because it needs to change some system files which are currently used by running processes, or changes in registry. You’ll be prompted with the yellow icon shield like in fig-1.
Powershell: How to Shift Time Offset of a Movie’s Subtitle
I usually go through my holidays with good movies. Some of the subtitles I downloaded do not have a correct timing with the video soundtrack. And it makes me re-adjust the subtitle whenever I re-play old movies. Since I do not want to install extra software or use websites to change my file whenever I get this problem, I decided to make it work in powershell. Continue reading “Powershell: How to Shift Time Offset of a Movie’s Subtitle”
Find all SNMP Settings of Windows Machine in Powershell
SNMP has a long history with Microsoft Windows. And Microsoft now said that it has been deprecated (moreover, snmp v1 or v2 is less secure than the latest snmp v3, but windows natively doesn’t support version 3 till now) and recommend using CIM for managing hardware and software layers. In this article, we will find the SNMP community string by batch method and powershell method. Continue reading “Find all SNMP Settings of Windows Machine in Powershell”
Set Windows Service Permission to Non-Administrator Accounts
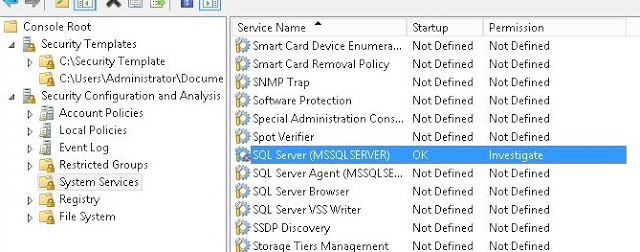
Service related operations such as start/stop/restart windows services are usually assigned to Administrators. Sometimes, you might need to delegate these tasks to non-admin users. In this article, I will show the 4 methods to set the service’s permission to any user account/service account. I will use SQL service (MSSQLSERVER) in domain environment.
Method-1: Using Powershell Module (from TechNet Script Repository, easiest but modules are not trusted by Microsoft)
Method-2: Using subinacl.exe (from Official Microsoft Download, need to install executable locally on computer, an easy method)
Method-3: Using built-in security configuration template in MMC console (do not need to install executable, easy with GUI but more steps are needed)
Method-4: Using built-in service control manager command line (difficult, prone-to-errors if manually configured)
Method-1: Using Powershell Module
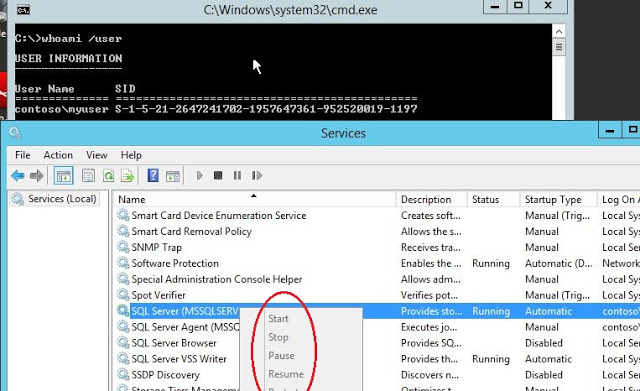
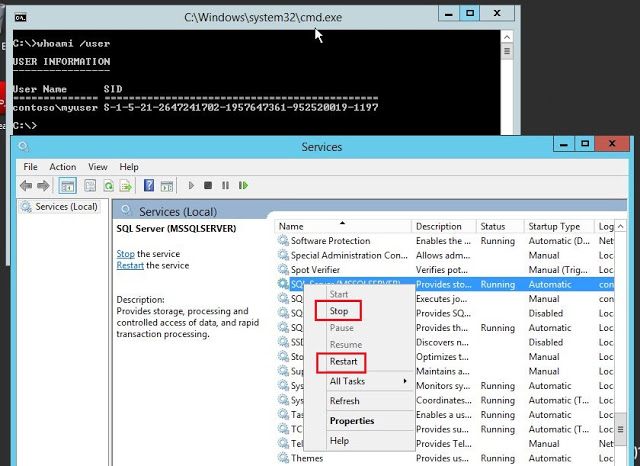
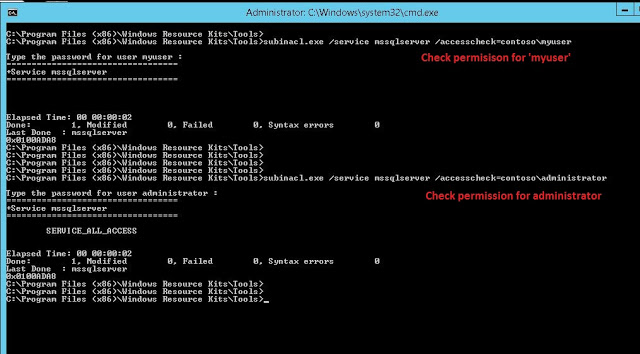
Edit: As of Aug,2021, I found that PowershellAccessControl module is no longer available on microsoft gallery. So, alternatively you can download it from github. Extract the zip file and rename the folder name PowerShellAccessControl-master to PowerShellAccessControl and move it to C:\Program Files\WindowsPowerShell\Modules. Before we start, let’s see the SQL service restart option is gray-out for ‘myuser’. See Fig-1.
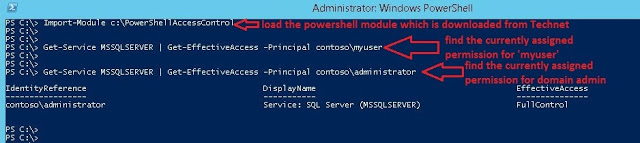
Open the powershell and check the current service permission for ‘myuser’. To do this, make Get-service and pipeline into Get-EffectiveAccess. Type the following command.
Get-Service MSSQLSERVER | Get-EffectiveAccess -Principal contosomyuser
You can also check the service permission for domain admin account.
Get-Service MSSQLSERVER | Get-EffectiveAccess -Principal contosoadministrator
See Fig-2.
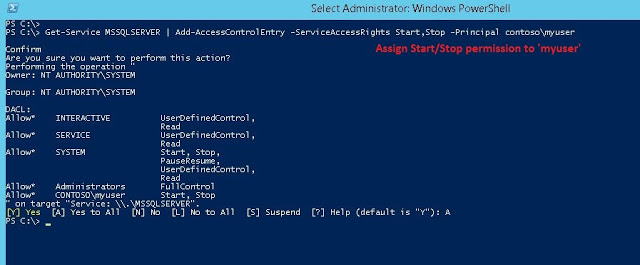
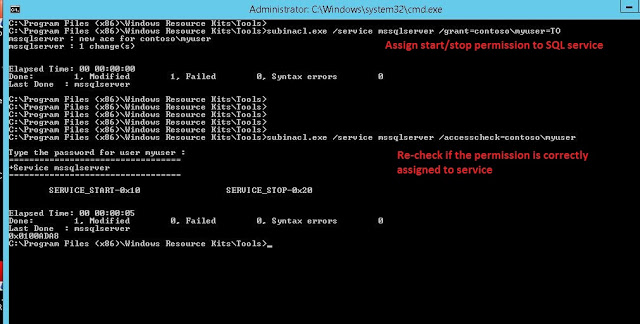
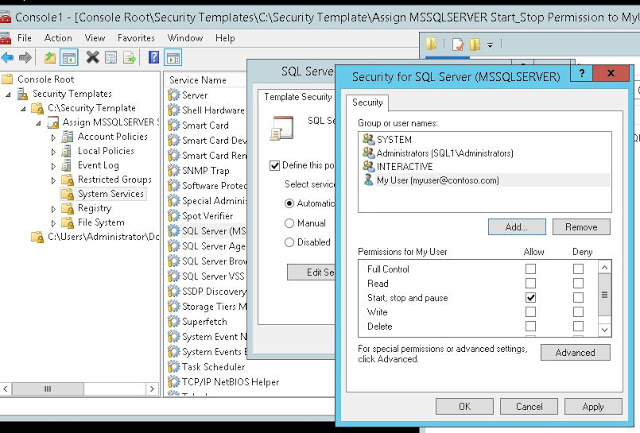
Now, give the user start/stop permission of MSSQLSERVER. See Fig-3.
Get-Service MSSQLSERVER | Add-AccessControlEntry -ServiceAccessRights Start,Stop -Principal contosomyuser
You can see that the ‘myuser’ now has the start/stop/restart permission on SQL service. See Fig-4.
|
Alias
|
Description
|
|
F
|
Full Control
|
|
R
|
Generic Read
|
|
W
|
Generic Write
|
|
X
|
Generic eXecute
|
|
L
|
Read controL
|
|
Q
|
Query Service Configuration
|
|
S
|
Query Service Status
|
|
E
|
Enumerate Dependent Services
|
|
C
|
Service Change Configuration
|
|
T
|
Start Service
|
|
O
|
Stop Service
|
|
P
|
Pause/Continue Service
|
|
I
|
Interrogate Service
|
|
U
|
Service User-Defined Control Commands
|
-
Create new security template (in which security settings of service is defined)
-
Create new security database with newly created security template
-
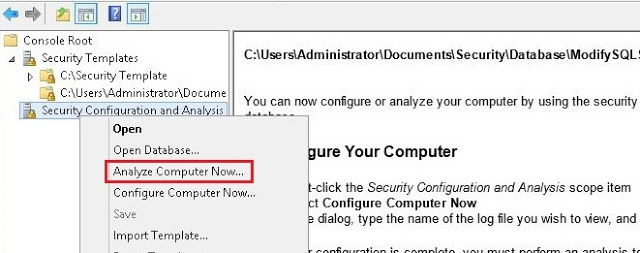
Analysis the current configuration with the security database and find the conflicts
-
Apply the security configuration
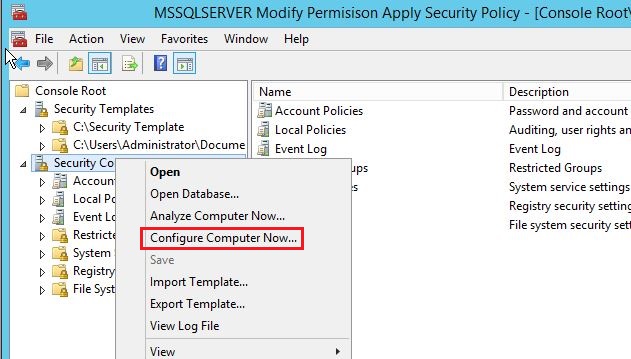
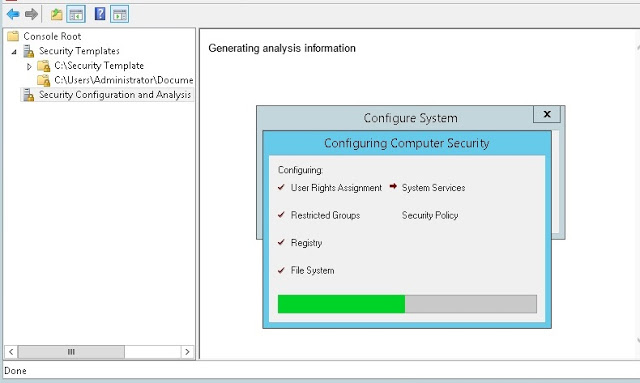
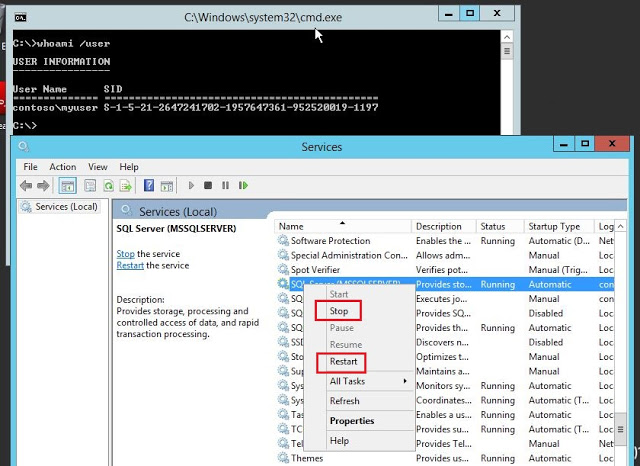
Now, you can start/stop the SQL service with our normal user account.
So, we will check the current permission of SQL service by the following command.
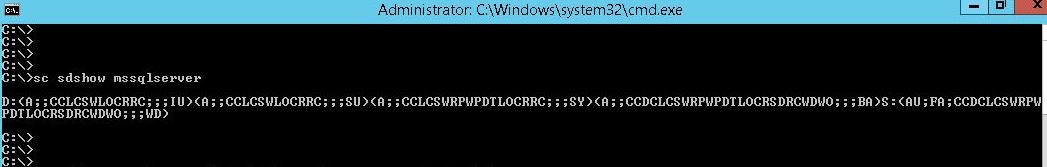
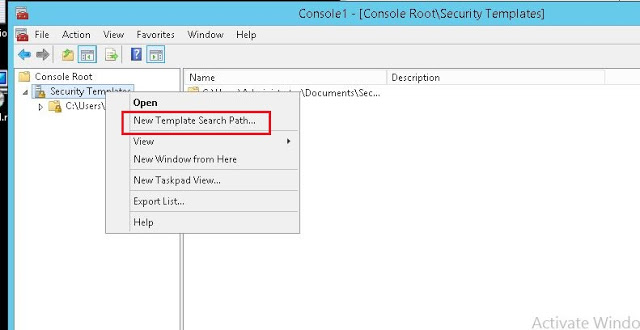
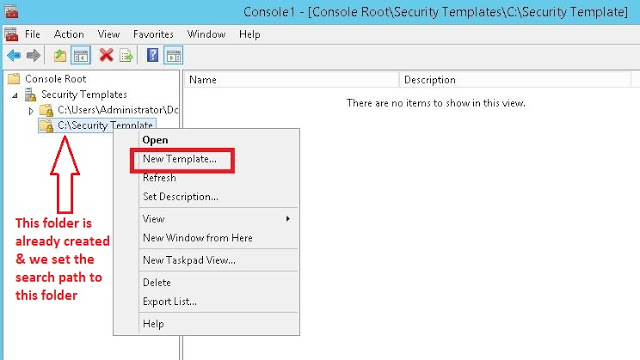
- Open MMC Console
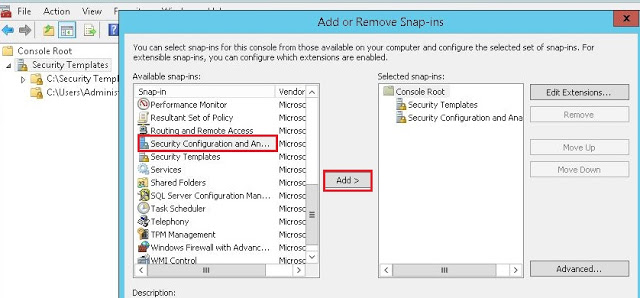
- Add “Security Templates” and “Security Configuration and Analysis” Snap-ins (Fig-11)
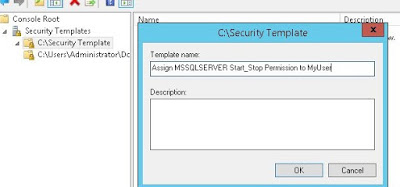
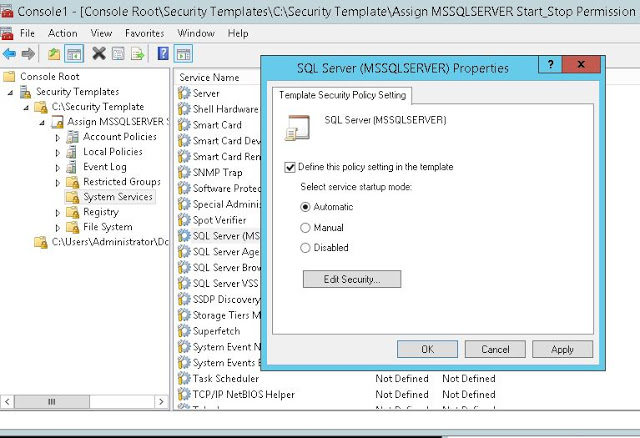
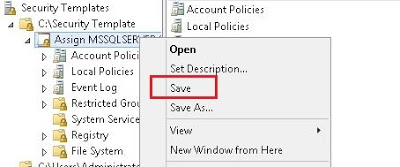
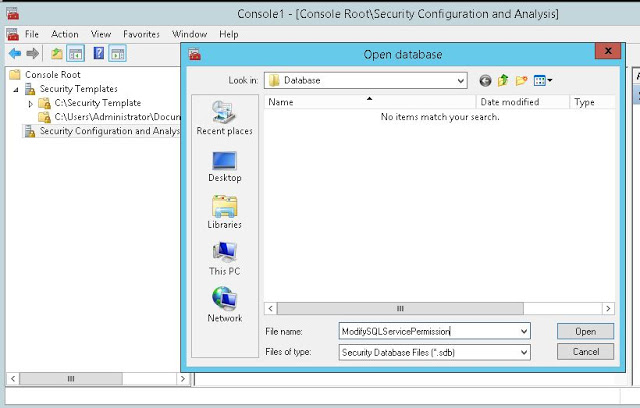
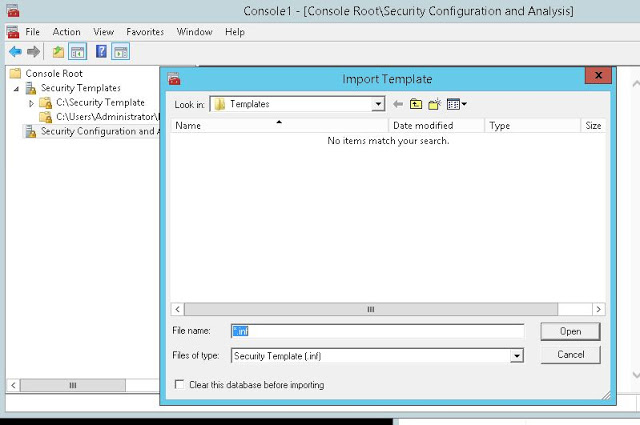
- Set the template path, create new template with desired settings and save the template (Fig-12,13,14,15,16)
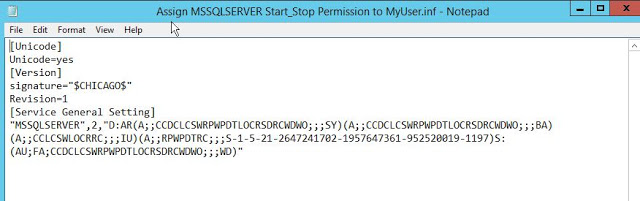
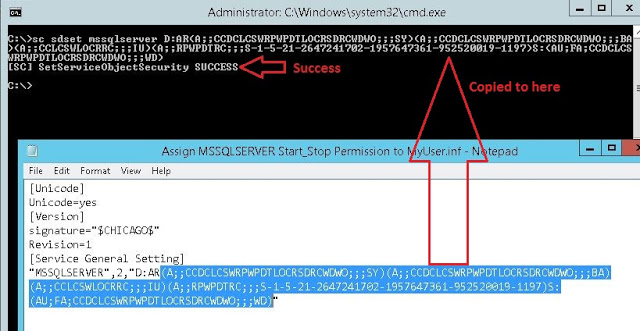
The command completes successfully. And user now has start/stop permission on SQL service. See Fig-27.
Active Directory Recycle Bin: Restore Deleted Objects or Wipe Off your Bin ?
Active Directory Recycle Bin is available from Server 2008R2 but it is disabled by default and it is one of the most useful feature for system admins in that he can restore any directory objects (user/computer or system accounts) that he mistakenly deleted.
You need Active Directory Administrative Center Console and forest functional level 2008R2 as a minimum to use this.
For the restore process, you can use GUI or powershell. For permanent deletion, powershell is the way to go. Also, there is tombstone lifetime and deleted object lifetime depending on how long you want to keep the deleted objects. Continue reading “Active Directory Recycle Bin: Restore Deleted Objects or Wipe Off your Bin ?”
